Plan Mode
Introduction
Plan Mode is designed to make "planning" a first-class citizen in the development workflow: complete requirement clarification, solution design, task breakdown, and execution coordination within the IDE without switching between multiple tools. Plan provides a lightweight, interactive AI collaboration approach that weaves capabilities like MCP, Skills, and SubAgents into a pluggable matrix, supporting both agile collaboration for small teams and customized governance for large projects.
Why Choose Plan
The Dilemma of Traditional AI Assistants
Imagine a familiar scenario:
You're developing a feature and tell the AI assistant: "Help me implement a shopping cart with CRUD operations and checkout." The AI starts working—it creates a file, writes some code, then... it creates another file and writes more code.
Ten minutes later, you discover:
- The data structure design is strange and doesn't align with your existing user system
- State management uses a library you've never used before
- Three files have completely inconsistent naming styles
- Your custom MCP, Skills, SubAgents weren't used as expected
- Most critically, it missed the coupon functionality
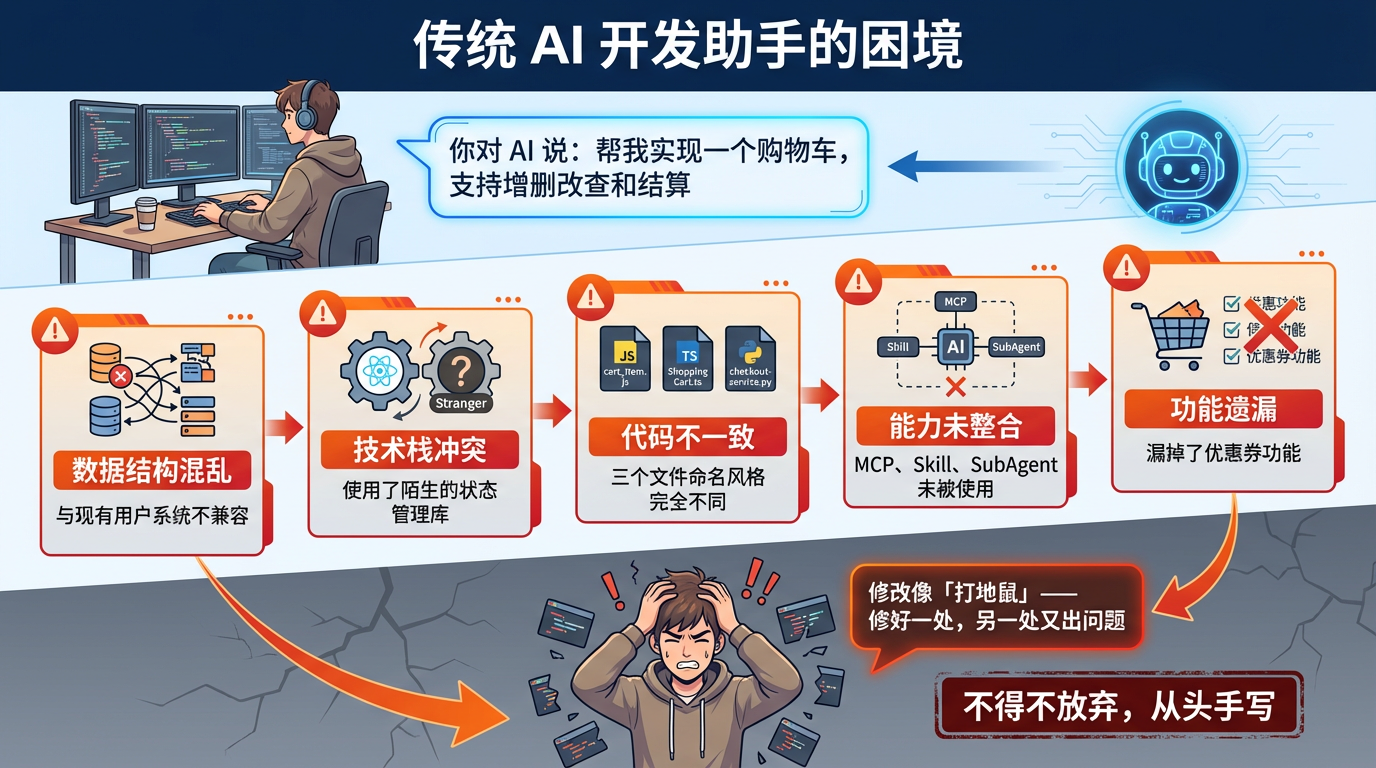
What's the root cause? The AI starts executing immediately upon receiving instructions without first aligning requirements, breaking down tasks, or confirming direction—missing a critical step: planning.
Plan Mode's Solution
CodeBuddy inserts a "planning" phase between "understanding" and "execution"—thinking through what to do, how to do it, and how many steps before executing.
| Pain Point | Traditional Mode | Plan Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Deviation | AI's implementation direction doesn't match user expectations | Requirement clarification phase aligns expectations |
| Unpredictability | Users can't foresee what AI will do | Solution preview, reviewable before execution |
| High Correction Cost | Each modification may introduce new problems | Complete planning, avoiding iterations |
| Context Loss | AI gradually "forgets" the original intent in long conversations | Persistent plan, traceable state |
Plan Mode vs Craft Mode: When to Use Which?
Plan and Craft are not mutually exclusive choices, but two collaboration modes for different scenarios. Understanding their differences can double your development efficiency.
| Dimension | Plan Mode | Craft Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Working Method | Plan first then execute, clarify solution before coding | Execute directly, respond quickly to instructions |
| Applicable Scenarios | Complex features, architecture design, multi-file coordination | Local modifications, single-file optimization, bug fixes |
| Output Format | Complete solution (requirements + technical + design + tasks) | Direct code results |
| Controllability | High - review and adjust solution before execution | Medium - adjust while executing |
| Extension Capabilities | Intelligent orchestration of MCP/Skill/SubAgent | On-demand extension calls |
Typical Scenarios for Plan Mode:
- 🏗️ Building New Features from Scratch - Requires clear technology selection, architecture design, and implementation path
- 🔄 Multi-file Coordinated Changes - Involves multiple modules, requires unified technical solution guidance
- 🎨 UI/UX Design and Implementation - Requires designing visual style and interaction logic before coding
- 🔧 Legacy Project Refactoring - Requires understanding existing architecture to ensure new features comply with project standards
- 📋 Complex Task Breakdown - Requires decomposing large requirements into executable steps
Typical Scenarios for Craft Mode:
- 🐛 Quick Bug Fixes - Problem is clear, requires quick identification and resolution
- ✨ Single-file Local Adjustments - Small scope of changes, direct execution is more efficient
- 📝 Code Refactoring and Optimization - Improving existing code
- 🔍 Code Explanation and Understanding - Understanding what a piece of code does
Core Value of Plan Mode:
- Planning Accuracy - Ensures AI truly understands your requirements through progressive clarification dialogue
- Solution Comprehensiveness - Outputs complete solutions including requirement analysis, technical architecture, visual design, and task breakdown
- Execution Controllability - Review and adjust solutions before code generation, avoiding later refactoring
- Extension Collaboration - Intelligent orchestration of MCP, Skills, SubAgents and other extensions to generate customized solutions
- Knowledge Reusability - Completed Plans are saved as Markdown, reusable as project knowledge base
Accessing and Selecting Plan Mode
- Open the sidebar and select Plan Mode.
- At the entry point, you can view the list of saved plans or create a new plan.
- If project plans already exist, you can open them directly; incomplete plans retain their context and execution progress.
| Select Plan Mode | New Plan Entry |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Plan Overview |
|---|
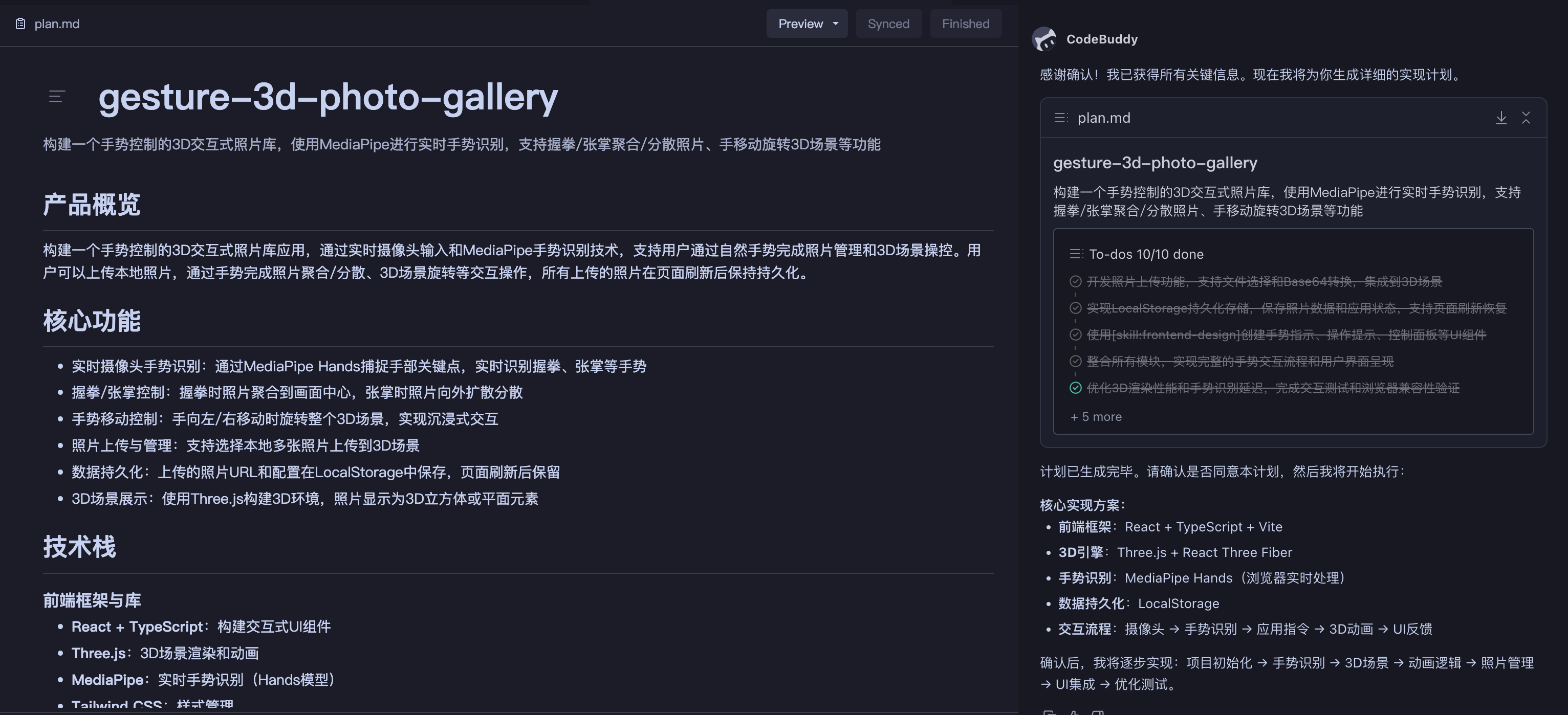 |
Usage: The Five-Step Plan Lifecycle
Plan divides a collaboration session into five phases, each supporting human-AI collaboration and image prompts, helping you complete the loop from idea to implementation within the IDE.
mermaid
flowchart LR
A[Requirement Clarification] --> B[Solution Development]
B --> C[Solution Edit/Confirm]
C --> D[Solution Implementation]
D --> E[Solution Complete]
style A fill:#e6f3ff
style B fill:#fff3e6
style C fill:#e6ffe6
style D fill:#ffe6e6
style E fill:#f3e6ff
Step 1: Requirement Clarification (Prepare State)
In this phase, AI helps you clarify requirement boundaries through progressive dialogue, ensuring both parties have a consistent understanding of the task.
Specific Operations:
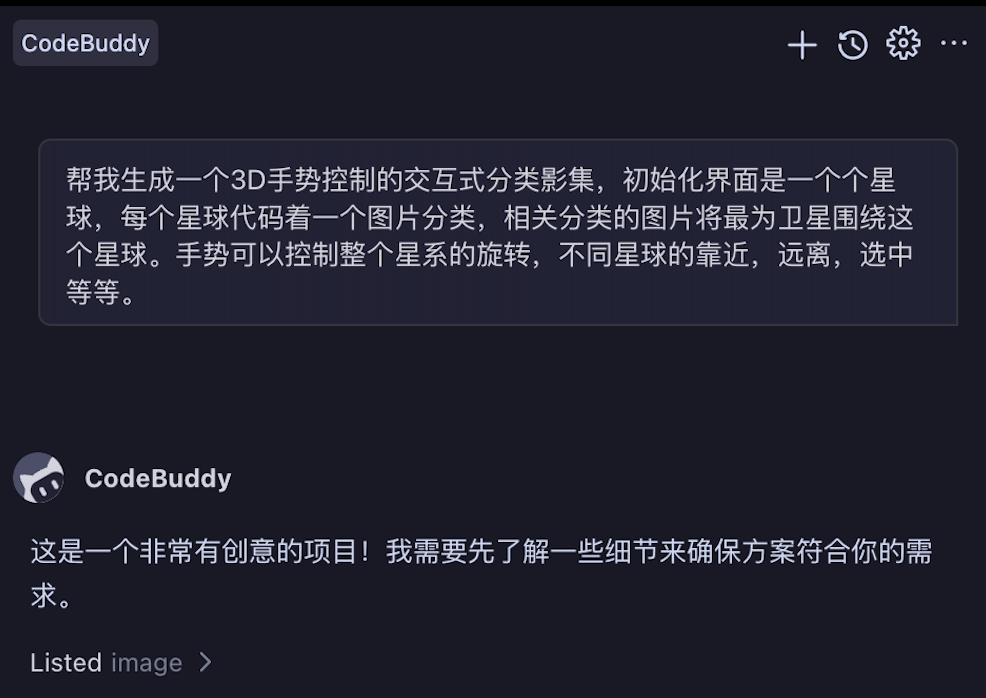
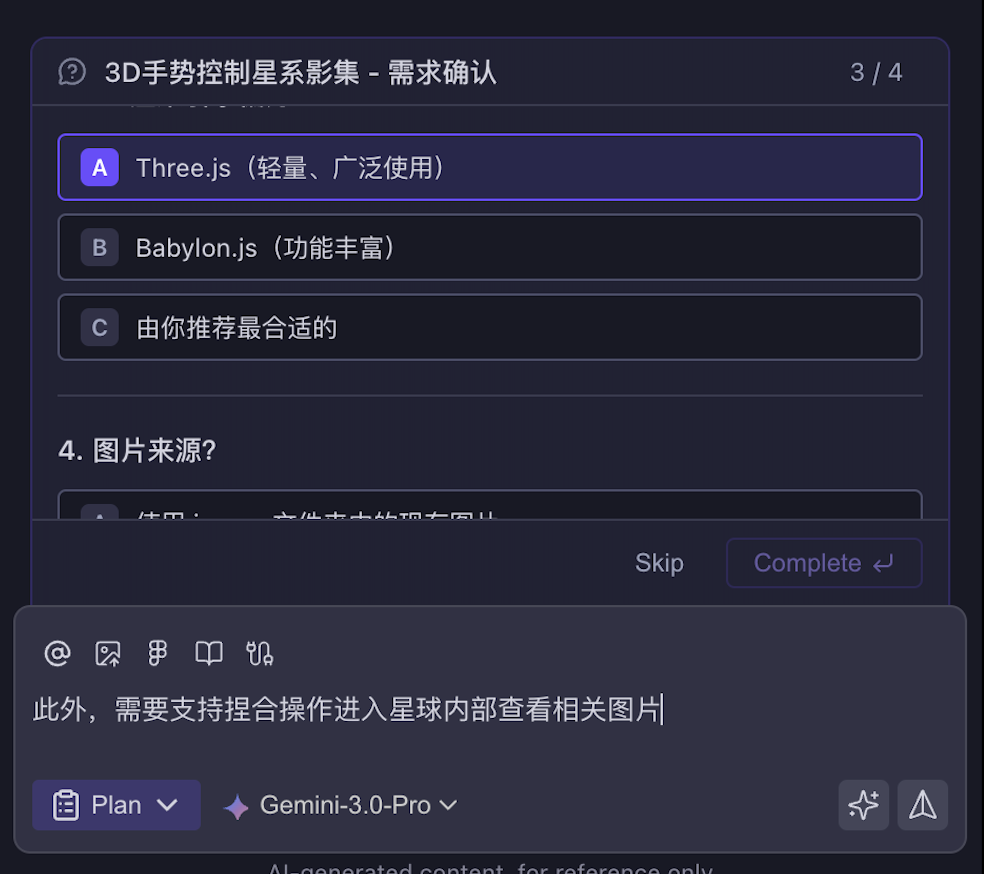
- Describe Requirements - Describe your goals or paste requirement documents in the input box
- Answer Clarification Questions - AI will ask 1-2 key questions to confirm tech stack, feature scope, constraints, etc.
- Confirm Requirements - After answering all questions, AI generates a requirement summary; proceed to the next step after confirmation
| AI Asks Clarification Questions | Options for User Selection |
|---|---|
 |  |
Tips:
- Provide as specific context as possible (tech stack, project structure, expected results, etc.)
- You can directly paste requirement documents or design mockup screenshots
- The quality of clarification questions directly affects the accuracy of subsequent solutions
Step 2: Solution Development (Prepare State)
After requirements are confirmed, AI generates a complete solution draft. This is the core of Plan Mode—thinking through everything before execution.
Solution Generation Process:
Plan will first provide an implementation outline based on your task requirements, then search for relevant code, designs, documentation, etc. in the existing project to generate a solution draft.
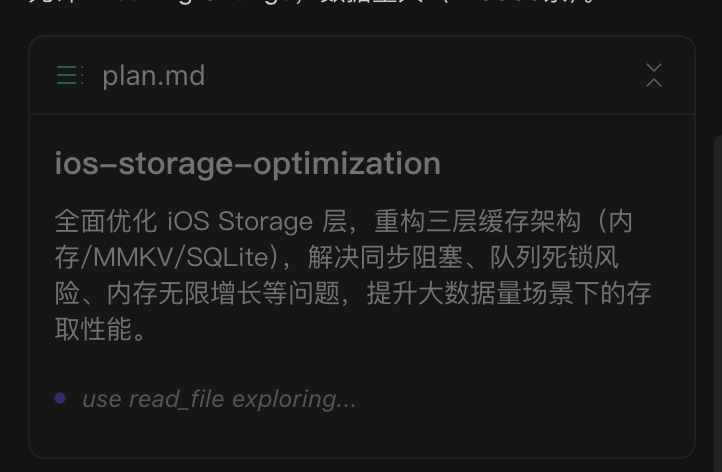
Solution Contents:
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Requirement Analysis | Extracts core value, feature boundaries, and expected outputs |
| Technical Solution | Technology selection, architecture design, key components, and data flow |
| Visual Design | UI style, interaction logic, color scheme (if applicable) |
| Task List | Executable step checklist, marking dependencies and priorities |
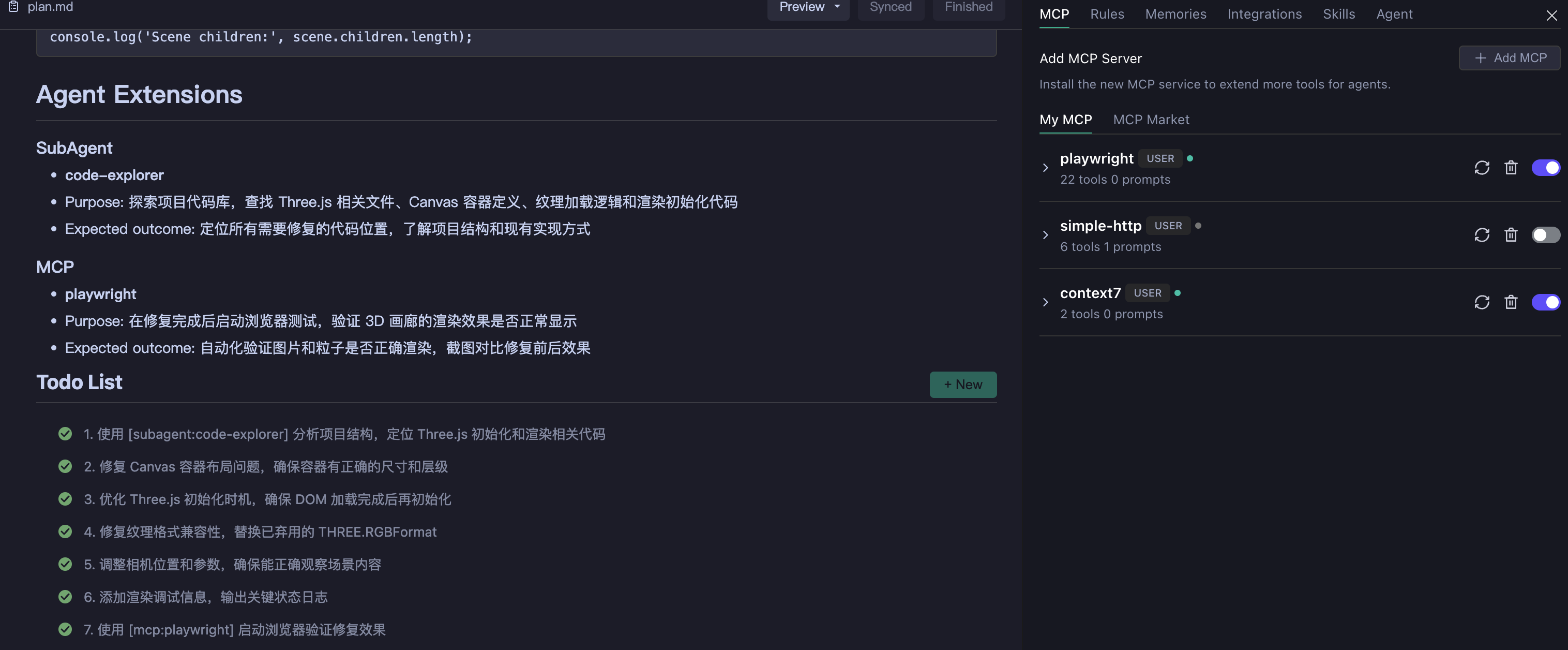
| Extension Capabilities | Recommended MCP/Skill/SubAgent and their purposes |
AI Intelligently Orchestrates Your Extensions:
- Analyzes task requirements, automatically matches appropriate MCP, Skills, SubAgents
- Explains the role and expected output of each extension in the solution
- Avoids hallucination calls, only uses extensions you've configured
Step 3: Solution Edit/Confirm (Ready State)
After generating the solution, you can review, edit, and confirm. This is the key phase for "predictability before execution"—correct the direction before code generation to avoid later refactoring.
Editable Content:
| Edit Type | Operations |
|---|---|
| Body Content | Adjust descriptions, add constraints, include reference links |
| Technical Solution | Modify technology selection, adjust architecture design |
| Task List | Insert/delete/reorder tasks, add execution details |
| Extension Capabilities | Add/remove plugins or agents to adapt to new scenarios |
| Markdown Editing | Update Task List |
|---|---|
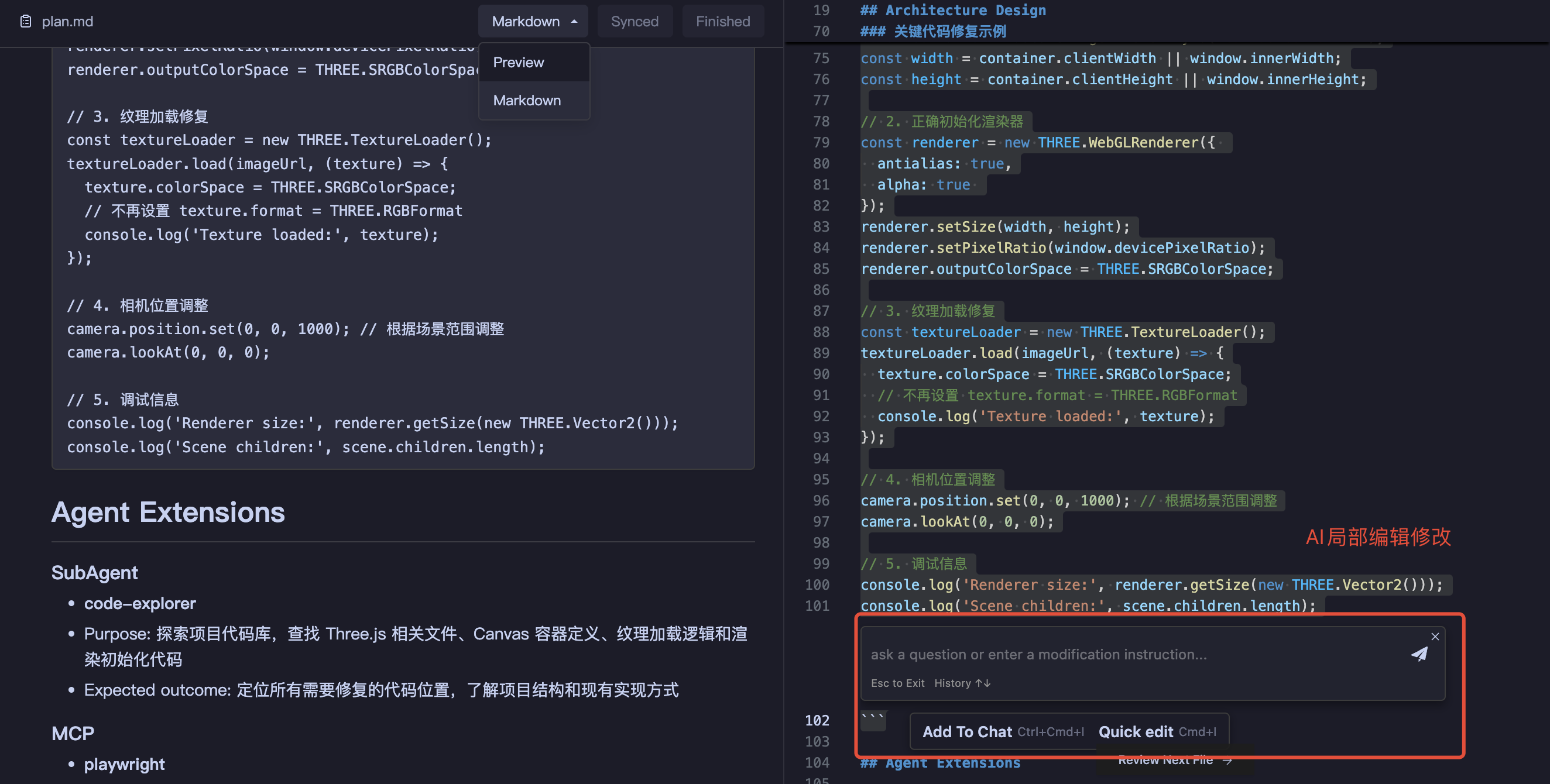 | 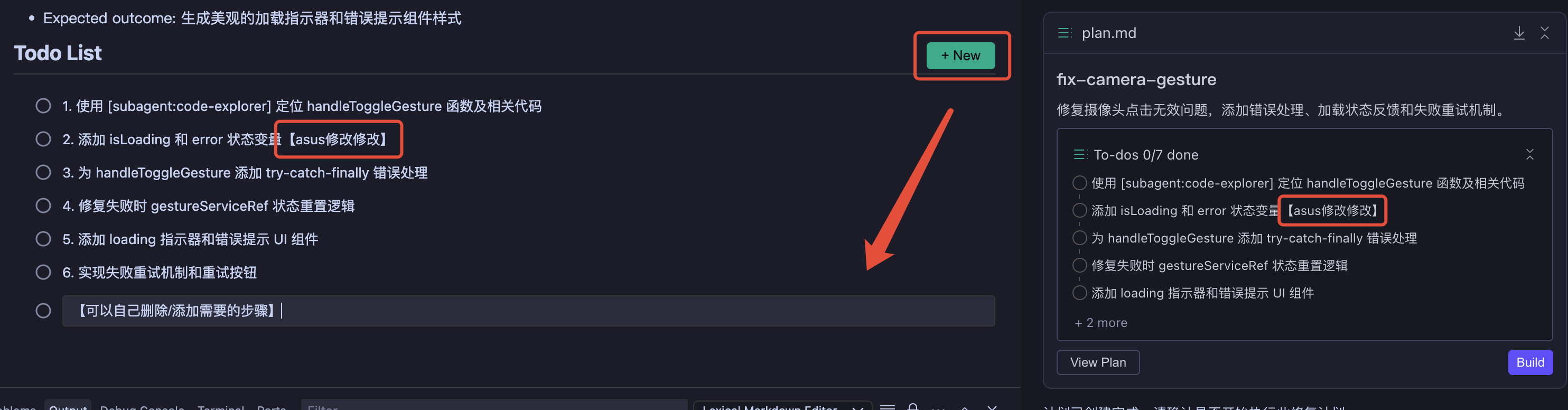 |
| Design Configuration Editing | Solution Extension Configuration |
|---|---|
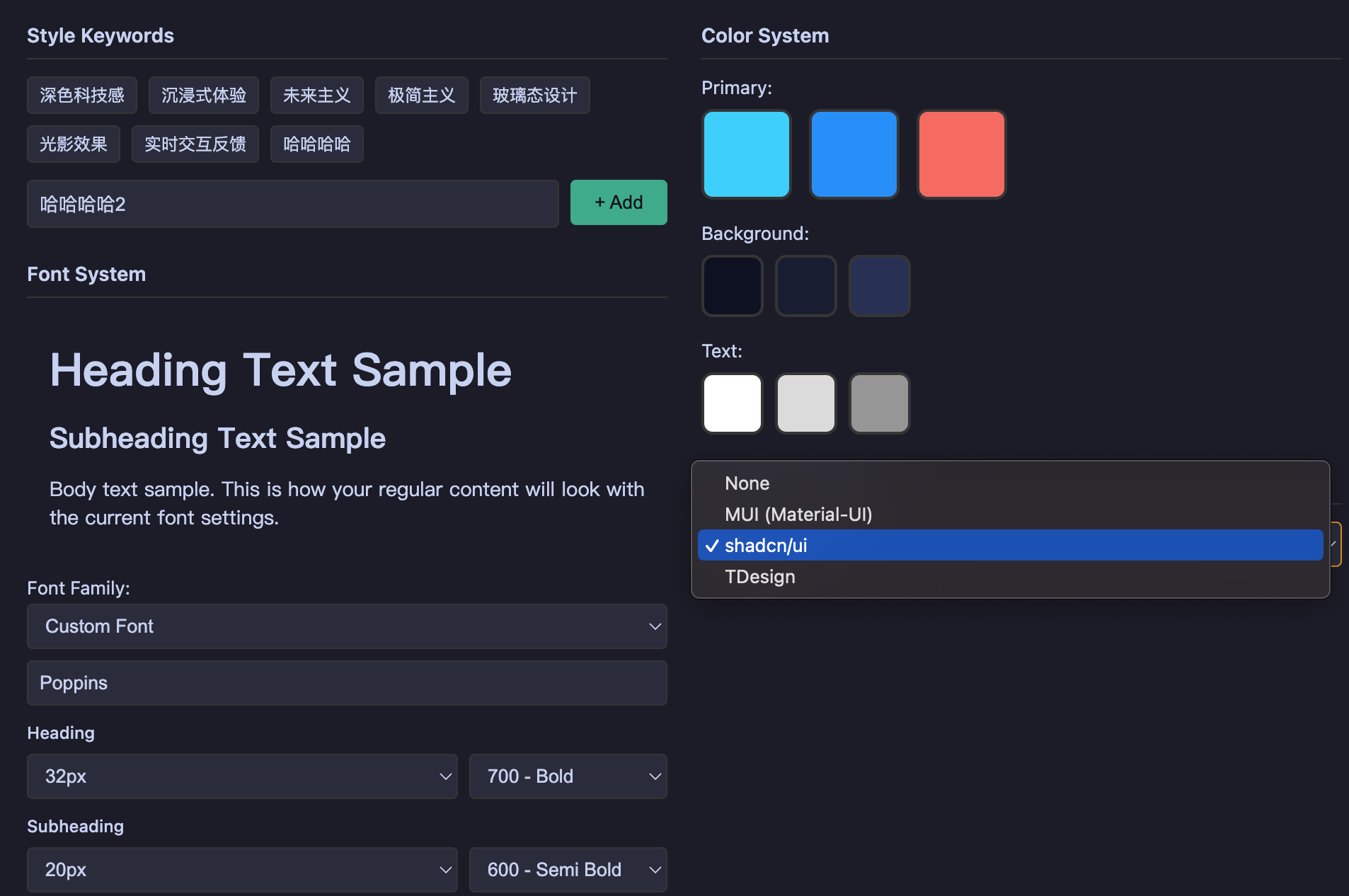 |  |
Pre-execution Confirmation Checklist:
- Does the technical solution align with the project's existing architecture?
- Is the task breakdown complete? Is the dependency order correct?
- Are the design specifications consistent with existing UI styles?
- Is the extension capability selection reasonable?
Step 4: Solution Implementation (Building State)
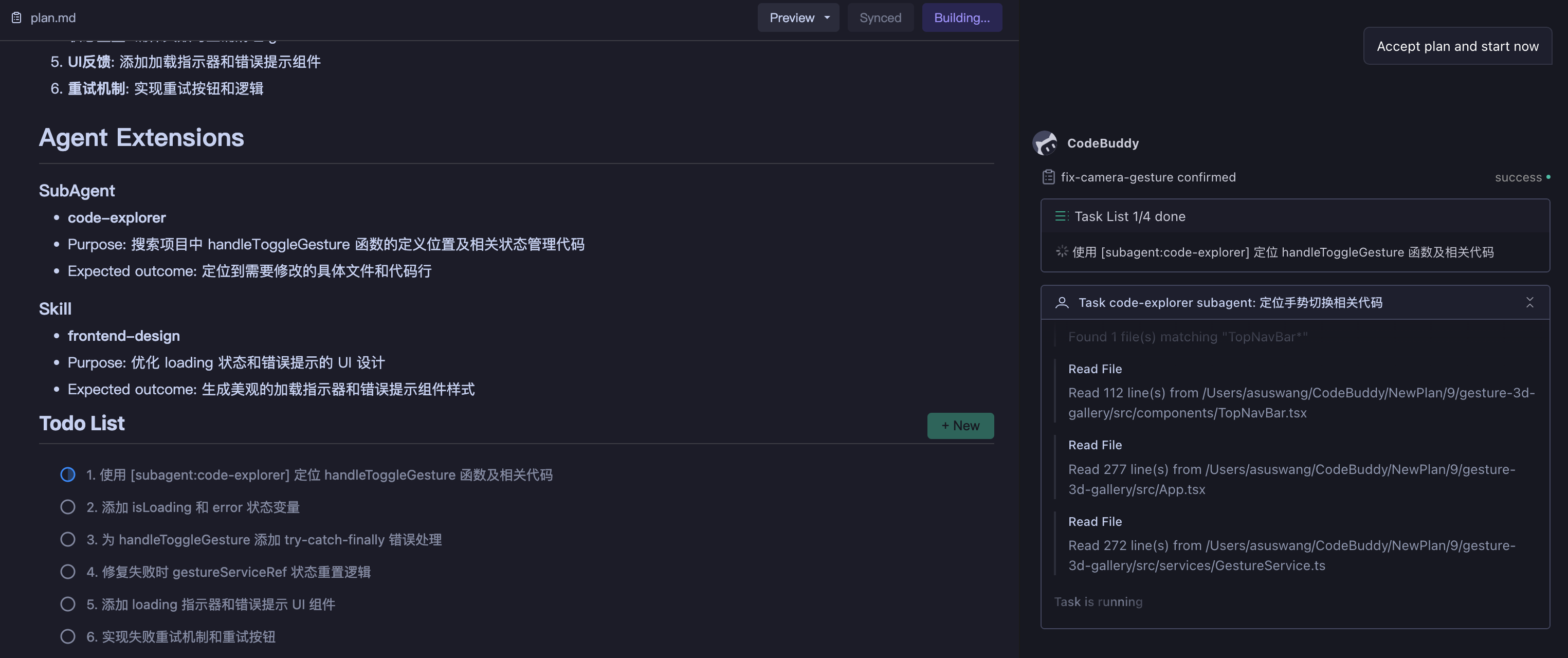
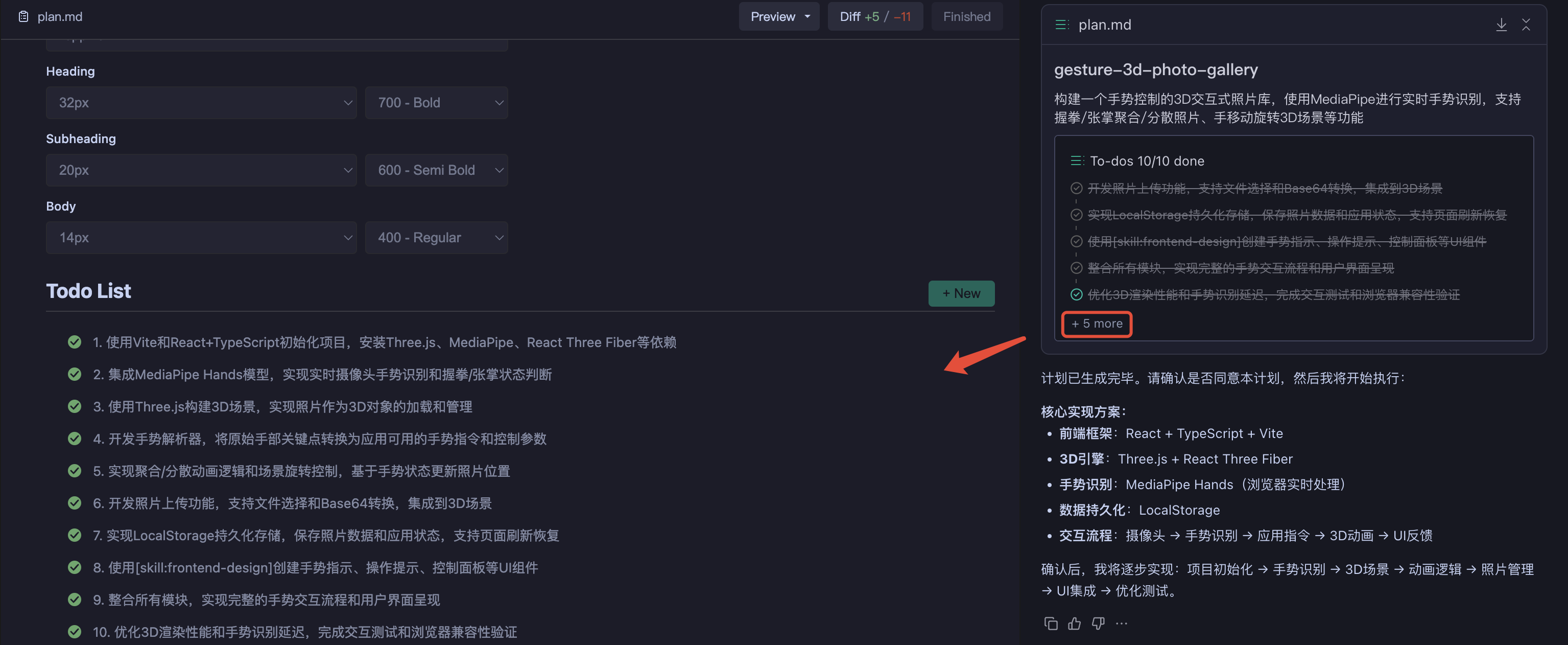
After clicking "Start Execution", the plan enters the execution phase. AI executes tasks step by step according to the task list and provides real-time progress feedback.
Execution Process:
- State Transition - Plan state changes to
Building, tasks execute in order - Progress Feedback - AI marks status after completing each task; you can view progress in real-time
- Interruption Handling - Can pause at any time during execution to propose new requirements or adjust direction
- Deep Extension Invocation - AI deeply invokes MCP, Skills, and other extensions according to the plan
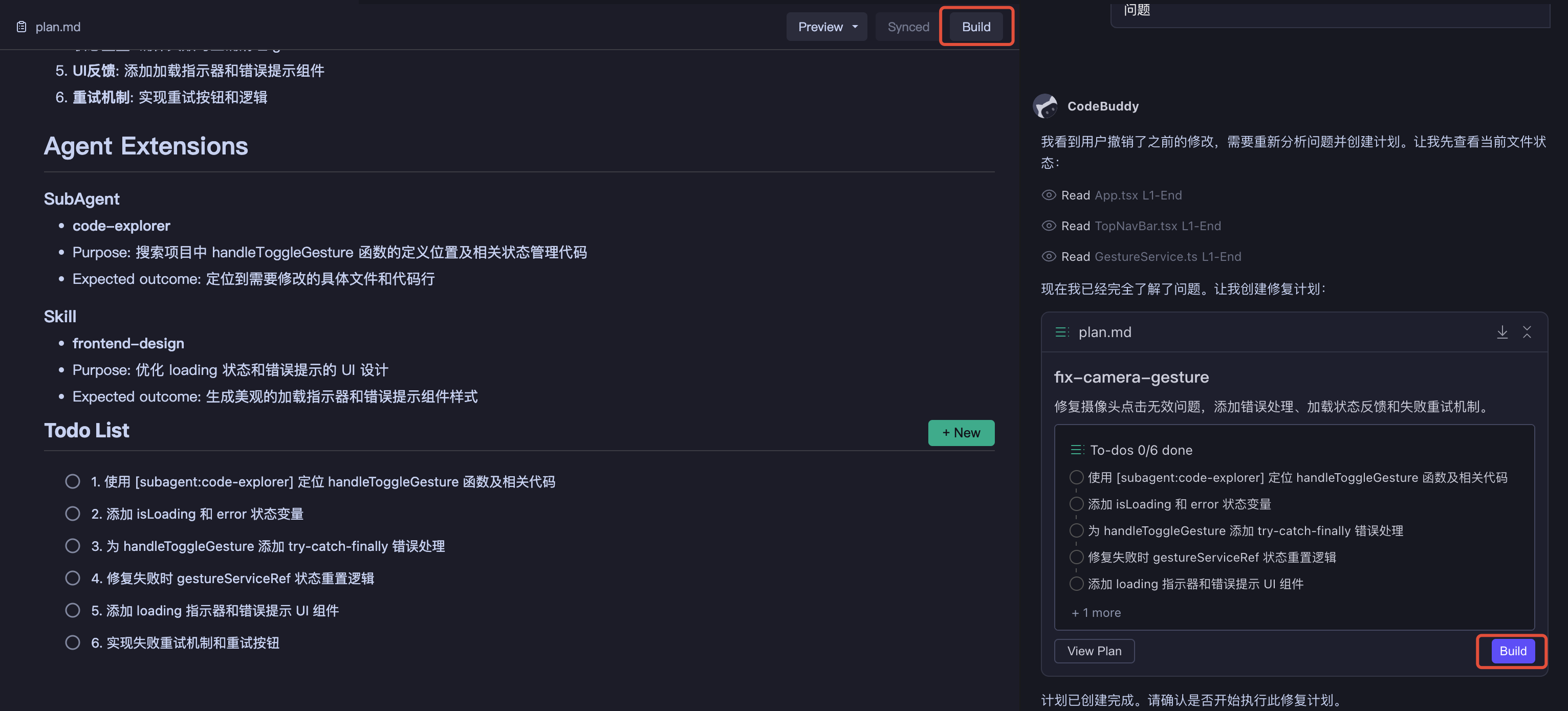
| Execution Status | Process Results |
|---|---|
 |  |
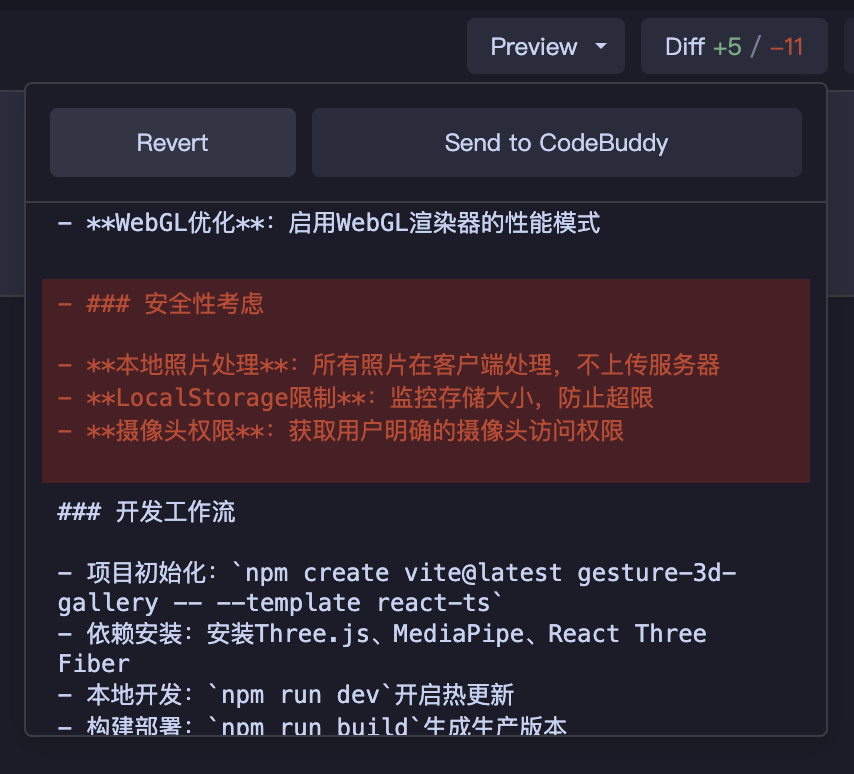
Adjustments During Execution:
- Fine-tune Solution - Can modify body content in the editing area; diff will highlight changes
- Switch to Craft - For local issues, switching to Craft Mode for quick fixes is more efficient
- Interruption Recovery - When new requirements arise, AI pauses the current plan and resumes after handling them
Step 5: Solution Complete (Finished State)
After all tasks are completed, the plan enters the finished state.
Post-completion Operations:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| View Results | View generated code and modified files in the editor |
| Archive Plan | Plan is automatically saved as a Markdown file in .codebuddy/plans/ |
| Export and Share | Download plan file to share with team or continue iterating |
| Reuse Knowledge | Historical plans can be referenced as context to help AI quickly understand project background |
| Save and Complete | Download Plan |
|---|---|
 | 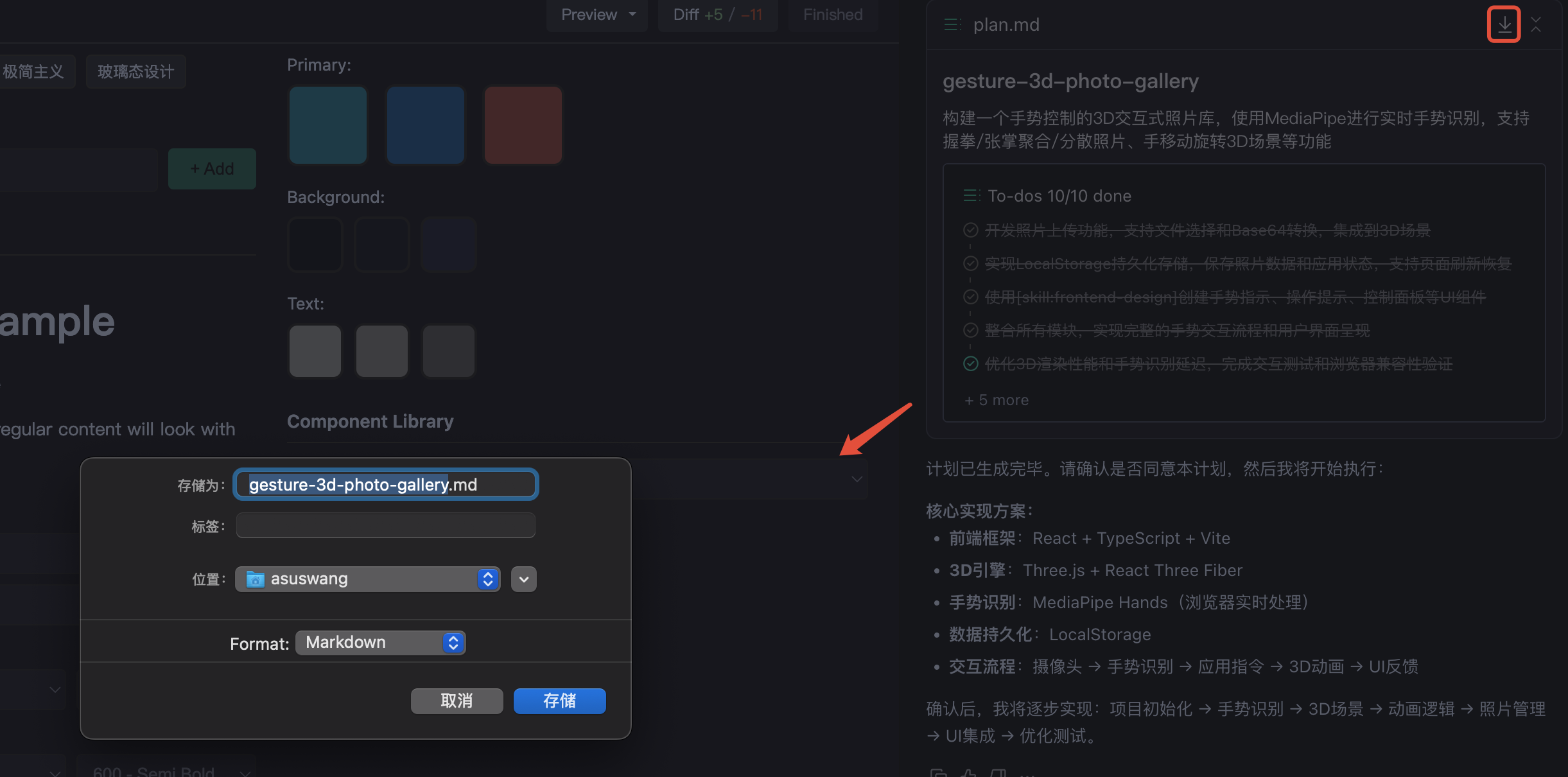 |
Usage Principles
Task Granularity Control
| Practice | Reason | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Single Plan Focuses on Single Feature Module | AI maintains stronger consistency within limited context | Overly large Plans lead to inconsistent naming, mixed interface styles, state management conflicts |
| Complete One Feature Module Before Starting Another | Verifiable intermediate deliverables facilitate problem identification | Multiple incomplete Plans running in parallel increase context confusion |
| Let AI Break Down Complex Requirements | AI can reasonably divide boundaries based on technical dependencies | Manual forced splitting may break natural coupling between modules |
Review Value During Preview Phase
Careful review after solution generation but before execution is the key phase to avoid later refactoring.
| Review Dimension | Checkpoints | Correction Cost Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Solution | Aligns with project's existing architecture? Technology selection reasonable? | Preview modification: Nearly zero / Post-code modification: May require refactoring |
| Task Breakdown | Missing key steps? Dependency order correct? | Preview modification: Text adjustment / Discovered during execution: Requires interruption and re-planning |
| Design Specifications | Consistent with existing UI style? Naming follows conventions? | Preview modification: Add constraints / Post-code: Batch renaming |
Core Principle: Correct direction before code generation to avoid later refactoring.
Collaborative Role of Extensions
Extensions (Skills, MCP, SubAgents, Integration) are not standalone tools, but form a collaborative matrix with Plan Mode:
| Extension Type | Mechanism | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Skills | Inject domain knowledge and best practices into planning context | frontend-design improves UI design quality |
| MCP | Connect to external services, obtain real-time data and latest documentation | Context7 retrieves framework's latest API documentation |
| SubAgents | Handle specific types of complex subtasks | debug-with-logger systematic problem diagnosis |
| Integration | Connect deployment and database infrastructure | CloudBase/CloudStudio one-click deployment |
Extensions are injected into context during Plan generation phase; AI intelligently selects based on task requirements and explicitly references them in the todolist.
Reuse Value of Plans
Completed Plans are saved in the .codebuddy/plans directory with the following reuse value:
- Context Transfer: New tasks can reference historical Plans to quickly establish project background understanding
- Token Savings: Avoid repeatedly describing existing architecture and specifications
- Knowledge Accumulation: Form project-level decision records and technical solution library
Usage Recommendations:
- Reference historical Plans in new conversations to help AI quickly understand project background
- Save successful architecture designs and technology selections as templates for reuse in similar future features
Flexible Switching Between Plan and Craft
Plan and Craft are not mutually exclusive choices, but partners that can be flexibly switched—use Plan to think through architecture first, then use Craft to quickly handle execution details.
| Scenario | Recommended Mode | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Macro Architecture Design | Plan | Requires complete requirement analysis and task breakdown |
| Multi-file Coordinated Changes | Plan | Requires unified technical solution guidance |
| Building New Features from Scratch | Plan | Requires clear implementation path |
| Local Detail Adjustments | Craft | Small scope of changes, no complete planning needed |
| Single Function Optimization | Craft | Clear context, direct execution is more efficient |
| Quick Bug Fixes | Craft | Problem identification is clear, no task breakdown needed |
Rule of Thumb: Use Plan for architecture-level changes, use Craft for detail-level adjustments.
