Context
@ Mentions
What is Context
In CodeBuddy IDE, Context refers to additional information you provide when conversing with AI, helping the AI better understand your requirements and generate code that meets your expectations. By using the @ symbol, you can reference various types of context content, including files, folders, documents, Git changes, and more.
Using context effectively can significantly improve the quality of AI responses, enabling AI to generate code based on the actual situation of your project and your specific needs.
@ Mentions
Use the @ symbol to quickly reference various types of context. After typing @, the system displays a list of available context types.
How to Use
- Type
@in the chat input - Use arrow keys to browse suggestions
- Press
Enterto select - If you select a category item (like Files & Folders), the list will be filtered to show the most relevant items in that category
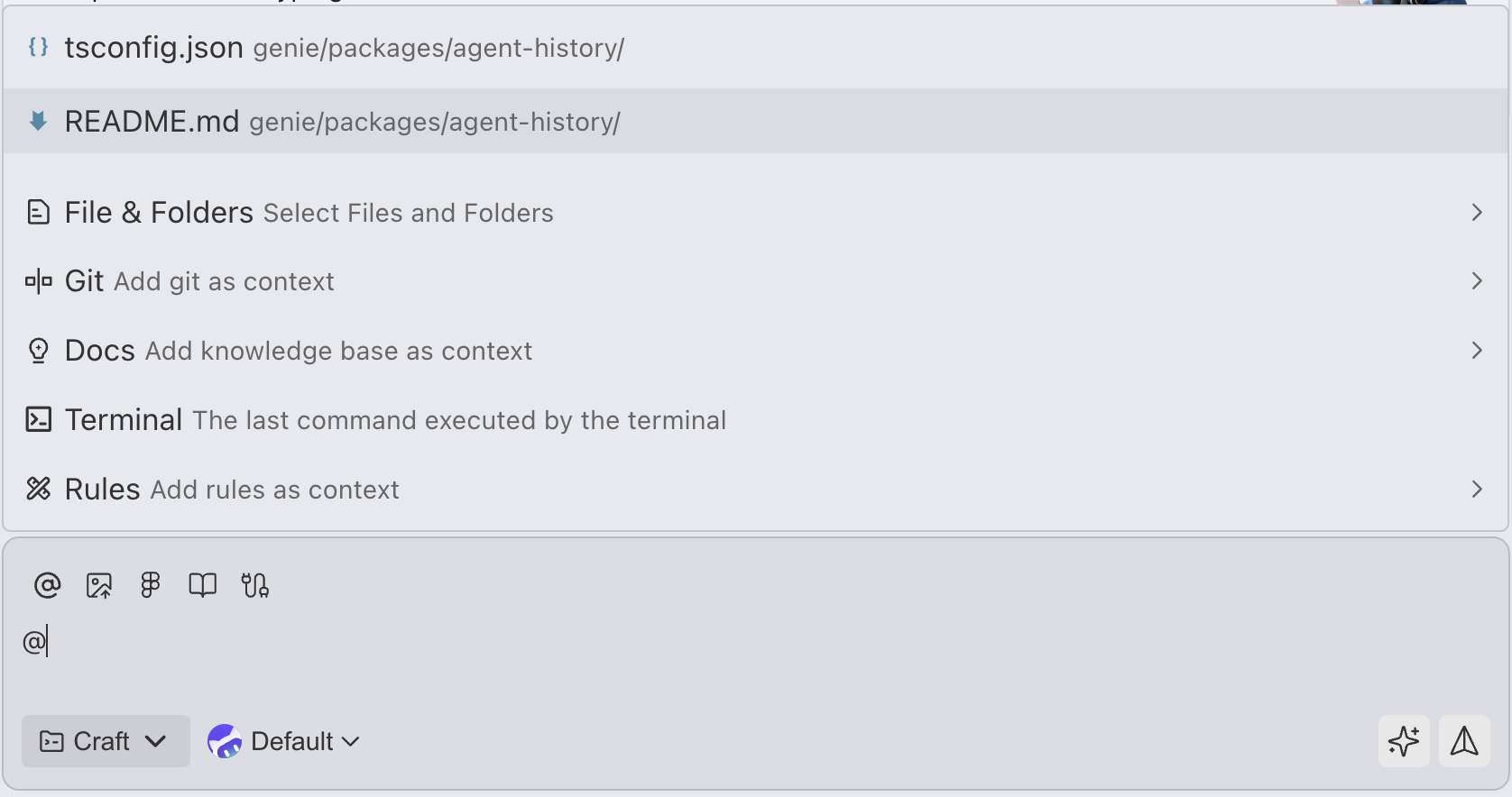
@Files & Folders - Files and Folders
@Single File
To reference an entire file as context:
- Type
@in the chat input - Select @Files & Folders
- Enter the filename to search
- Select the target file
Quick access: You can also drag a file directly from the sidebar into the chat input, or right-click and select "Add to CodeBuddy conversation" to quickly add it as context.
Usage Example
@src/components/Button.tsx Please help me add hover effects to this button component@Folders
When using @Folders to reference a folder, CodeBuddy provides the folder's path and a summary of its contents, helping the AI understand the project structure and available resources.
Navigate subfolders:
- After selecting a folder, type
/to enter the next level directory - Browse and select folders
Usage Example
@src/components/ Please help me refactor all components in this folder to use a consistent style system@Code - Code Snippets
Use the @Code symbol to reference specific code snippets, providing more fine-grained control than @Files & Folders.
Features
- Precisely reference specific functions, classes, or code blocks
- Avoid introducing unrelated code from the entire file
- Support referencing multiple code snippets across files
How to Use
- Select the code block you want to add to context, choose the auto-populated "Add to chat", or right-click and select "Add to CodeBuddy conversation"
Usage Example
@handleSubmit:10-20 This submit function needs form validation logic added@Code vs @Files & Folders
| Feature | @Code | @Files & Folders |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | Precise to function/class level | Entire file or folder |
| Context size | Smaller, only contains selected snippet | Larger, contains complete file content |
| Use case | Targeted modifications, refactoring specific features | Understanding overall structure, batch modifications |
@Docs - Documentation
The @Docs feature allows you to reference technical documentation to assist with code writing. CodeBuddy includes documentation for common frameworks and libraries, and you can also add custom documentation.
Using Existing Documentation
- Type
@Docsin the chat input - Browse the available documentation list
- Select relevant framework or library documentation
Built-in Documentation Examples
CodeBuddy includes some common documentation:
- WeChat Pay
- WeChat Mini Programs
- WeChat Mini Games
- Tencent Cloud API
Usage Example
@WeChat Mini Program How do I create a mini programAdding Custom Documentation
To add documentation that is not currently available:
- Select
@Docs - In "Add knowledge base as context"
- Enter the knowledge base name
@Git
@Git allows you to reference Git-related context, helping the AI understand code change history and current modification status.
Git Content You Can Reference
1. Uncommitted Changes
Reference file modifications in the current workspace that have not been committed:
@Git:uncommitted Please help me review these changes and check for potential issues2. Specific Commit
Reference historical commit records:
- Select
@Git - Select Workspace Changes or History Commits
@Git:commit:abc123 Please explain the main changes in this commit@Terminal - Terminal Commands
@Terminal allows you to reference terminal command output and execution information as context.
How to Use
- Execute commands in the terminal
- Type
@Terminalin the chat input - Select recently executed commands or their output
Usage Example
@Terminal:npm-test Tests failed, please help me analyze the errors and fix them@Rules - Coding Standards
@Rules allows you to reference project coding standards and conventions, ensuring AI-generated code meets team standards. Currently only supports @manual type rules.
Feature Description
Rules are guidance documents provided to AI, which can include:
- Coding style standards (such as naming conventions, code formatting)
- Architectural design principles
- Framework usage preferences
- Security standards
- Project-specific conventions
How to Use
- Type
@Rules - Select applicable standard documents
- AI will follow these standards when generating code
Usage Example
@Rules:coding-style Please rewrite this function according to our coding standards@Rules:architecture Please implement this new feature based on our architectural design principlesBest Practices
1. Precise Referencing, Avoid Redundancy
❌ Not recommended:
@entire project folder Please help me modify the login function✅ Recommended:
@src/auth/login.ts @src/components/LoginForm.tsx Please help me modify the login function2. Combine Multiple Context Types
Combine different types of context to provide more complete information:
@Files:config.ts @Docs:Express @Rules:api-design Please help me implement a RESTful API route3. Use @Code for Precise Modifications
When you only need to modify a specific function, use @Code instead of the entire file:
@Code:calculateTotal This calculation function has precision issues, please fix it4. Reference Git Changes for Code Review
Use Git context for self-review before committing:
@Git:uncommitted Please review these changes and check for performance issues or security vulnerabilities